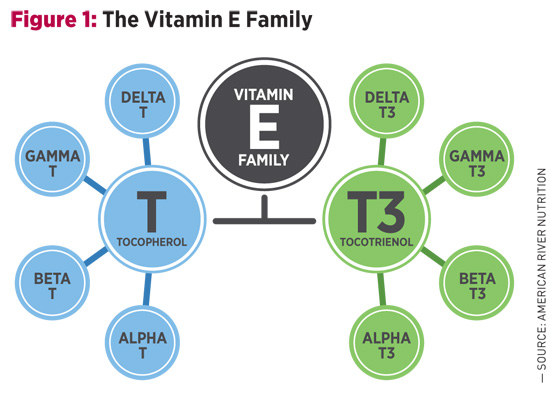
Although research on tocotrienols is well underway, few have heard of this important, albeit elusive, member of the vitamin E family. Tocotrienols were first discovered in the late 1950s and—originally thought to be tocopherols—were mislabeled with Greek letters such as epsilon and zeta.6 The mistake was recognized,7,8 but official designations in the Merck Index were not corrected until 2001.9,10 It’s not surprising, then, that tocotrienols are only now emerging into public view, and the timing is fortuitous. According to the US Census Bureau, older adults (age 65 and older) will soon outnumber children, and with increasing age comes a heightened risk of chronic conditions. Tocotrienols may help prevent and address aging concerns through their antioxidant properties.
Read More